Air sealing and insulation are two essential components of energy-efficient and comfortable buildings. They serve different but complementary purposes in improving the energy performance and comfort of a structure. Here’s a breakdown of each:
- Air Sealing:
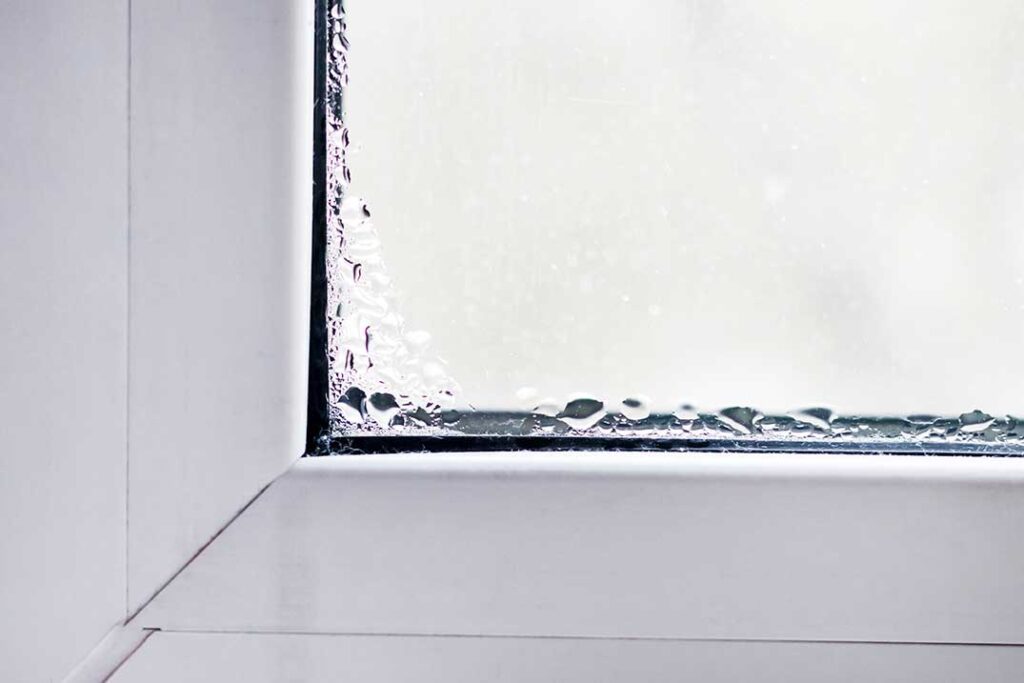
- Purpose: Air sealing refers to the process of sealing gaps, cracks, and openings in a building’s envelope to prevent the uncontrolled flow of outdoor air into the interior and indoor air escaping to the outside. The goal is to reduce air leakage, which can lead to energy waste, discomfort, and the potential for moisture and condensation issues.
- Materials and Techniques: Air sealing is typically achieved using materials like caulk, weatherstripping, foam sealants, and other sealing products. It involves sealing gaps around windows and doors, at wall penetrations (such as electrical outlets and pipes), in the attic, and around the foundation.
- Benefits: Air sealing helps to reduce drafts, improve indoor air quality, enhance energy efficiency, and prevent moisture-related problems. It makes the insulation more effective by creating a barrier that prevents conditioned air from escaping and outdoor air from entering.
- Insulation:
- Purpose: Insulation is a material that reduces the transfer of heat between the interior and exterior of a building. It helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature by slowing down the movement of heat through walls, ceilings, and floors. Insulation primarily deals with thermal performance and improving energy efficiency.
- Materials and Techniques: Various types of insulation materials are available, such as fiberglass, cellulose, foam board, and spray foam. Insulation is installed within the walls, ceilings, and floors of a building to provide a thermal barrier. The choice of insulation material and installation technique depends on factors like R-value, space constraints, and budget.
- Benefits: Insulation helps reduce heat loss during the winter and heat gain during the summer, thereby lowering heating and cooling costs. It enhances indoor comfort by maintaining a consistent temperature and can improve soundproofing as a secondary benefit.
In summary, air sealing and insulation work hand in hand to create an energy-efficient and comfortable building:
- Air sealing primarily focuses on preventing air leaks and drafts, which enhance energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and moisture control.
- Insulation primarily focuses on reducing heat transfer, which leads to improved thermal comfort and energy savings.
Both measures are crucial in creating a well-protected and energy-efficient building. They should be considered together when planning energy upgrades for a home or building, as one complements the other to maximize overall performance and comfort.